잔틴
화합물
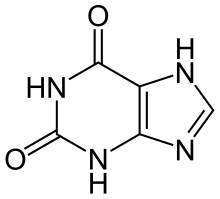
잔틴(영어: xanthine) 또는 크산틴(독일어: Xanthin)은 대부분의 인체 조직과 분비액, 다른 유기체에서 볼 수 있는 퓨린 염기이다. 수많은 각성제가 카페인과 테오브로민을 포함하여 잔틴에서 비롯된다.[2]
| |

| |
| 이름 | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC 이름
3,7-Dihydropurine-2,6-dione
| |
| 별칭
1H-Purine-2,6-dione
| |
| 식별자 | |
3D 모델 (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.653 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| 성질 | |
| C5H4N4O2 | |
| 몰 질량 | 152.11 g/mol |
| 겉보기 | White solid |
| 녹는점 | decomposes |
| 1 g/ 14.5 L @ 16 °C 1 g/1.4 L @ 100 °C | |
| 위험 | |
| NFPA 704 (파이어 다이아몬드) | |
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하면, 표준상태(25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa)에서 물질의 정보가 제공됨.
| |
잔틴은 퓨린 대사 방식의 산물이다.
- 구아닌 탈아미 노효소의 구아닌
- 잔틴 산화효소의 하이포잔틴
- 퓨린 뉴클레오시드 가인산분해효소(PNP)의 크산토신[3].
선별된 잔틴 편집
| 이름 | R1 | R2 | R3 | IUPAC 명명법 | 발견 위치 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 카페인 | CH3 | CH3 | CH3 | 1,3,7-trimethyl-1H-purine-2,6(3H,7H)-dione | 커피, 과라나, 마테, 차, 콜라 |
| 테오브로민 | H | CH3 | CH3 | 3,7-dihydro-3,7-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione | 초콜릿, 마테 |
| 테오필린 | CH3 | CH3 | H | 1,3-dimethyl-7H-purine-2,6-dione | 차, 초콜릿, 마테 |
| 파라잔틴 | CH3 | H | CH3 | 1,7-dimethyl-7H-purine-2,6-dione | 카페인을 소비해온 짐승 |
| 잔틴 | H | H | H | 3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione | 식물, 짐승 |
각주 편집
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 9968.
- ↑ Spiller, Gene A. (1998). 《Caffeine》. Boca Raton: CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-2647-8.
- ↑ Voet, Donald; Voet, Judith; Pratt, Charlotte (2008). "The Major Pathways of Purine Catabolism in Animals," Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level, p. 840.
같이 보기 편집
| 이 글은 화학에 관한 토막글입니다. 여러분의 지식으로 알차게 문서를 완성해 갑시다. |
