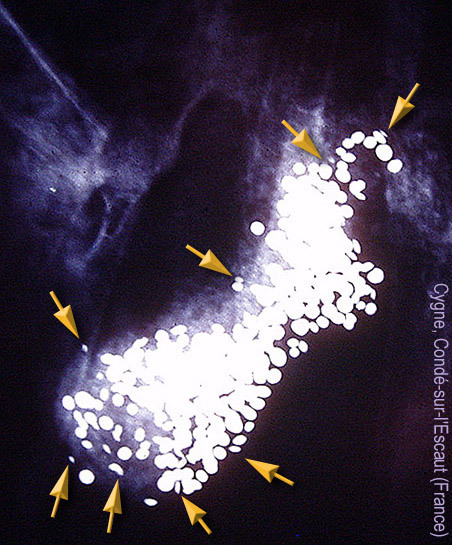
English: Radiography of a swan found dead in Condé-sur-l'Escaut (North of France), highlighting a large number of lead shot from hunting cartridge, and ingested with the
Grit. The swans that feed in front of hunters's huts or in front of shooting positions are very frequently victim of "waterfowl lead poisoning". Here the number of lead is exceptionally high (some hundreds), and caused the death of the animal (12 small lead pellets are enough to kill an adult swan within a few days. The poisoned swans were also more likely to collide with an obstacle (power line, for example) or vehicle. Their body will be a new source of environmental contamination of toxic lead. It is noted that a new swan population has recovered in the late 1990s in the marsh audomarois, but it feeds mainly on land, which is a source of conflict with the gardeners who cultivate drained areas and emergent marsh (Is this an adaptive behavior, the result of natural selection, with the appearance of a new behavior limiting the risk of ingesting lead pellets)
It should be noted that the occurrence and prevalence of lead poisoning avian sontplus higher in Europe and North America where they were first studied. See data collected by RAFAEL MATEO (Instituto de Investigación en Recursos Cinegéticos IREC, CSIC, UCLM, JCCM) for his presentation WILD BIRDS IN Lead Poisoning IN EUROPE AND THE REGULATIONS ADOPTED BY DIFFERENT COUNTRIES upon
Conference entitledIngestion of Spent Lead Ammunition; Implications for Wildlife and Humans (organized by the "Peregrine Fund" (Boise State University Idaho. May 12-15, 2008).
Proceedings of the conference, which led to the book: [https: / / www.createspace.com / 3382279 Ingestion of Spent Lead Ammunition from: Implications for Wildlife and Humans, co-written by Richard T. Watson, Mark Fuller, Mark Pokras, Grainger Hunt] 2009/04/28; ISBN/EAN13: 0961983957 / 9780961983956, 394 pages.
Français : Radiographie d'un cygne trouvés morts à Condé-sur-l'Escaut (Nord de la France) mettant en évidence un grand nombre de grenaille de plomb, provenant de cartouche de chasse, et ingérées avec le
grit. Les cygnes mangeant devant les huttes de chasse ou devant des postes de tirs très utilisés sont fréquemment victime du saturnisme. Ici le nombre de plomb est exceptionnellement élevé, et a causé la mort de l'animal. 12 billes de plomb suffisent généralemnt à tuer un cygne adulte en quelques jours. Les cygnes intoxiqués ont également plus de risque d'entrer en collision avec un obstacle (ligne à haute tension par exemple) ou un véhicule. Leur cadavre sera une nouvelle source de contamination environnementale. Il est à noter qu'une nouvelle population de cygnes s'est reconstitué à la fin des années 1990 dans le marais Audomarois (plus de 250 oiseaux vers 2008 selon la presse locale) , mais qu'elle se nourrit essentiellement sur terre, ce qui est source de conflit avec les maraichers qui cultivent les zones drainées et émergées du marais (voir
Article Voix du Nord, du Jeudi 2009/10/08, de Nicolas Faucon, intitulé "À Saint-Omer, ulcéré par les dégâts commis par les cygnes, un maraîcher assigne l'État")(S'agit il d'un comportement adaptatif, issu d'une sélection naturelle, avec apparition d'un nouveau comportement limitant le risque d'ingestion de billes de plomb).
Les flèches jaunes montrent des grains de plomb déjà très érodés. Il est possible que d'autres grains (totalement érodés et donc non visible sur cette radiographie) aient été antérieurement avalés par le cygne. Ici l'animal a du mourir en quelques jours, d'une intoxication aiguë (avec une agonie probablement très douloureuse, si l'on se rapporte à ce qu'on connait des symptômes du
saturnisme chez l'Homme).
Il est à noter que l'occurrence et la prévalence du saturnisme aviaire sont plus élevés en Europe qu'en Amérique du nord où ils ont d'abord été étudiés. Cf. données collectées par RAFAEL MATEO (Instituto de Investigación en Recursos Cinegéticos IREC ; CSIC, UCLM, JCCM) pour son exposé LEAD POISONING IN WILD BIRDS IN EUROPE AND THE REGULATIONS ADOPTED BY DIFFERENT COUNTRIES
lors de la
Conférence intitulée Ingestion of spent lead ammunition ; Implications for wildlife and humans (organisée par le "Peregrine fund" (Boise state University, Idaho. 12-15 mai 2008).
Actes de la conférence, qui ont donné lieu à l'ouvrage :
Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife and Humans, co-écrit par Richard T. Watson, Mark Fuller, Mark Pokras, Grainger Hunt 2009/04/28 ; ISBN/EAN13:0961983957 / 9780961983956 ; 394 pages.