피리딘
화합물
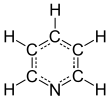
피리딘(Pyridine)은 벤젠의 CH 하나가 질소로 치환된 헤테로고리 화합물이다.
| |||
| |||

| |||
| 이름 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 우선명 (PIN)
Pyridine[1] | |||
| 체계명
Azabenzene | |||
| 별칭
Azine
Azinine 1-Azacyclohexa-1,3,5-diene | |||
| 식별자 | |||
3D 모델 (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.464 | ||
| EC 번호 |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| 성질 | |||
| C5H5N | |||
| 몰 질량 | 79.102 g·mol−1 | ||
| 겉보기 | Colorless liquid[2] | ||
| 냄새 | Nauseating, fish-like[3] | ||
| 밀도 | 0.9819 g/mL[4] | ||
| 녹는점 | −41.6 °C (−42.9 °F; 231.6 K) | ||
| 끓는점 | 115.2 °C (239.4 °F; 388.3 K) | ||
| Miscible | |||
| log P | 0.73[5] | ||
| 증기 압력 | 16 mmHg (20 °C)[3] | ||
| 짝산 | Pyridinium | ||
굴절률 (nD)
|
1.5093 | ||
| 점도 | 0.88 cP 25 °C | ||
| 2.2 D[6] | |||
| 위험[8] | |||
EU classification (DSD) (outdated)
|
Flammable (F) Harmful (Xn) | ||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R20 R21 R22 R34 R36 R38 | ||
| NFPA 704 (파이어 다이아몬드) | |||
| 인화점 | 21 °C (70 °F; 294 K) | ||
| 폭발 한계 | 1.8–12.4%[3] | ||
유해화학물질 허용농도 (TLV)
|
5 ppm (TWA) | ||
| 반수 치사량 또는 반수 치사농도 (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
891 mg/kg (rat, oral) 1500 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 1580 mg/kg (rat, oral)[7] | ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
9000 ppm (rat, 1 hr)[7] | ||
| NIOSH (미국 건강 노출 한계): | |||
PEL (허용)
|
TWA 5 ppm (15 mg/m3)[3] | ||
REL (권장)
|
TWA 5 ppm (15 mg/m3)[3] | ||
IDLH (직접적 위험)
|
1000 ppm[3] | ||
| 관련 화합물 | |||
관련 amines
|
Picoline Quinoline | ||
관련 화합물
|
Aniline 피리미딘 Piperidine | ||
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하면, 표준상태(25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa)에서 물질의 정보가 제공됨.
| |||
형성
편집역사
편집피리딘 불순물은 동물의 뼈와 기타 유기 물질을 가열함으로써 초기 연금술사들에 의해 만들어졌지만,[9] 최초의 문서화된 기록은 스코틀랜드의 과학자 토머스 앤더슨에 의해 이루어졌다.[10][11]
각주
편집- ↑ 《Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book)》. Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. 141쪽. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ Shimizu, S.; Watanabe, N.; Kataoka, T.; Shoji, T.; Abe, N.; Morishita, S.; Ichimura, H., 〈Pyridine and Pyridine Derivatives〉, 《울만 공업화학 백과사전(Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry)》, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_399
- ↑ 가 나 다 라 마 바 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. “#0541”. 미국 국립 직업안전위생연구소 (NIOSH).
- ↑ Lide, p. 3–474
- ↑ “Pyridine - CAS#:110-86-1”. 《ChemSrc》. 2020년 1월 8일.
- ↑ 《RÖMPP Online – Version 3.5》. 《Thieme Chemistry》 (Stuttgart: Georg Thieme). 2009.
- ↑ 가 나 “Pyridine”. 《Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH)》. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ “Pyridine MSDS”. 《fishersci.com》. Fisher.
- ↑ Weissberger, A.; Klingberg, A.; Barnes, R. A.; Brody, F.; Ruby, P.R. (1960). 《Pyridine and its Derivatives》 1. New York: Interscience.
- ↑ Anderson, Thomas (1849). “On the constitution and properties of picoline, a new organic base from coal-tar”. 《Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh》 16: 123–136.
- ↑ Anderson, T. (1849). “Producte der trocknen Destillation thierischer Materien” [Products of the dry distillation of animal matter]. 《Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie》 (독일어) 70: 32–38. doi:10.1002/jlac.18490700105.
외부 링크
편집- 위키미디어 공용에 피리딘 관련 미디어 분류가 있습니다.
| 이 글은 화학에 관한 토막글입니다. 여러분의 지식으로 알차게 문서를 완성해 갑시다. |