헥사메틸렌테트라민
화합물
(메텐아민에서 넘어옴)
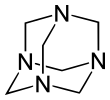
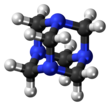
헥사메틸렌테트라민(hexamethylenetetramine) 또는 메텐아민(methenamine, hexamine, urotropin)은 헤테로고리 유기화합물의 하나로, 화학식은 (CH2)6N4이다. 이 흰 결정 화합물은 물과 극유기용제에 매우 잘 녹는다. 아다만테인과 같은 새장과 같은 구조를 지니고 있다. 플라스틱, 약, 고무 첨가물 등 다른 화합물의 합성에 유용하다. 280 °C의 진공에서 승화된다.
| |||
| 이름 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC 이름
1,3,5,7-Tetraazatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane
| |||
| 별칭
Hexamine; Methenamine;
Urotropine; 1,3,5,7- tetraazaadamantane, Formin, Aminoform | |||
| 식별자 | |||
3D 모델 (JSmol)
|
|||
| 2018 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.642 | ||
| EC 번호 |
| ||
| E 번호 | E239 (방부제) | ||
| 26964 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Methenamine | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| 성질 | |||
| C6H12N4 | |||
| 몰 질량 | 140.186 g/mol | ||
| 겉보기 | White crystalline solid | ||
| 냄새 | Fishy, ammonia like | ||
| 밀도 | 1.33 g/cm3 (at 20 °C) | ||
| 녹는점 | 280 °C (536 °F; 553 K) (sublimes) | ||
| 85.3 g/100 mL | |||
| 용해도 | Soluble in 클로로포름, methanol, 에탄올, 아세톤, 벤젠, xylene, 에터 | ||
| chloroform에서의 용해도 | 13.4 g/100 g (20 °C) | ||
| methanol에서의 용해도 | 7.25 g/100 g (20 °C) | ||
| ethanol에서의 용해도 | 2.89 g/100 g (20 °C) | ||
| acetone에서의 용해도 | 0.65 g/100 g (20 °C) | ||
| benzene에서의 용해도 | 0.23 g/100 g (20 °C) | ||
| 산성도 (pKa) | 4.89[1] | ||
| 약리학 | |||
| J01XX05 (WHO) | |||
| 위험 | |||
| 주요 위험 | Highly combustible, harmful | ||
| GHS 그림문자 |  
| ||
| 신호어 | 경고 | ||
| H228, H317 | |||
| P210, P240, P241, P261, P272, P280, P302+352, P321, P333+313, P363, P370+378, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (파이어 다이아몬드) | |||
| 인화점 | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) | ||
| 410 °C (770 °F; 683 K) | |||
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하면, 표준상태(25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa)에서 물질의 정보가 제공됨.
| |||
합성, 구조, 반응
편집헥사메틸렌테트라민은 1859년 알렉산드르 부틀레로프에 의해 발견되었다.[2][3] 폼알데하이드와 암모니아를 결합시켜서 산업적으로 준비된다.[4] 반응은 기체상과 용액으로 수행할 수 있다.
각주
편집- ↑ Cooney, A. P.; Crampton, M. R.; Golding, P. (1986). “The acid-base behaviour of hexamine and its N-acetyl derivatives”. 《J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2》 (6): 835–839. doi:10.1039/P29860000835.
- ↑ Butlerow, A. (1859). “Ueber einige Derivate des Jodmethylens” [On some derivatives of methylene iodide]. 《Ann. Chem. Pharm.》 (독일어) 111 (2): 242–252. doi:10.1002/jlac.18591110219. In this paper, Butlerov discovered formaldehyde, which he called "Dioxymethylen" (methylene dioxide) [page 247] because his empirical formula for it was incorrect (C4H4O4). On pages 249–250, he describes treating formaldehyde with ammonia gas, creating hexamine.
- ↑ Butlerow, A. (1860). “Ueber ein neues Methylenderivat” [On a new methylene derivative]. 《Ann. Chem. Pharm.》 (독일어) 115 (3): 322–327. doi:10.1002/jlac.18601150325.
- ↑ Eller, K.; Henkes, E.; Rossbacher, R.; Höke, H. (2000). 〈Amines, Aliphatic〉. 《Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry》. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001. ISBN 9783527306732.
외부 링크
편집- 위키미디어 공용에 헥사메틸렌테트라민 관련 미디어 분류가 있습니다.